Over 2 billion pallets are in circulation in the United States alone. This staggering number underscores the critical role pallets play in modern commerce. When I first learned this fact early in my logistics career, it completely changed my perspective on pallet management. Today, I’m excited to take you on a deep dive into this nuanced world, exploring its hidden ecosystem, innovations, and global impact.

Source: researchgate.net
Table of Contents
- The Hidden Ecosystem of Pallet Logistics
- Pallet Design Innovation
- The Circular Economy of Pallets
- The Psychology of Pallet Management
- Geopolitical Implications of Pallet Standards
- Pallet Management Services: Beyond the Basics
- The Environmental Impact of Pallet Choices
- The Role of Pallets in Disaster Relief and Humanitarian Logistics
The Hidden Ecosystem of Pallet Logistics
Pallet management is a vast, intricate network that keeps goods moving efficiently across the globe. It’s far more complex than most people realize, involving a multi-tiered system of manufacturers, distributors, and recyclers. Every aspect of a pallet’s journey, from design to end-of-life considerations, plays a crucial role in modern commerce.
The sheer scale of the pallet industry is mind-boggling. The global pallet market was valued at $79.0 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach a staggering $110.6 billion by 2027. This growth is driven by increasing global trade and the rise of e-commerce, which has forced retailers and manufacturers to expand their warehouses and increase stocks.
According to a recent industry report, global demand for pallets is forecast to increase 4.0% per year to 6.9 billion units in 2028, valued at $83.6 billion. [Source: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2024/10/28/2969826/28124/en/Pallets-Market-Report-2024-2033-Efforts-to-Address-Sustainability-Concerns-Reshaping-Markets-Further-Opportunities-for-Smart-Pallets.html]
This explosive growth has significant implications for businesses of all sizes. For those looking to optimize their inventory practices in this rapidly evolving landscape, our guide on Mastering the Walmart Marketplace offers valuable strategies for warehouse operations and inventory management.

Source: plasolutions.com
Pallet Design Innovation
The world of pallet design is in a constant state of evolution. Manufacturers are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, focusing on sustainability, durability, and efficiency. These innovations are reshaping the industry and improving supply chain operations worldwide.
Advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software is now used to optimize pallet structures for specific load requirements. This technology allows for precise customization, ensuring that each pallet is perfectly suited to its intended use. Material science advancements have led to the development of hybrid pallets combining wood, plastic, and metal components, offering the best properties of each material.
One of the most exciting developments in pallet engineering is the use of finite element analysis (FEA). This powerful tool simulates stress and strain on pallet designs under various load conditions, allowing engineers to identify and address potential weak points before a single pallet is produced. The result? Stronger, more efficient pallets that can withstand the rigors of modern supply chains.
I recently spoke with a major fruit supplier in the Pacific Northwest who switched from wood-block pallets to plastic pallets. The results were impressive: a significant reduction in pallet rejections by retailers, lower return fees, and decreased product waste due to the more uniform and damage-resistant nature of plastic pallets. It’s a perfect example of how innovative pallet design can have far-reaching effects on a company’s bottom line.
Biomimicry in Pallet Engineering
Nature-inspired designs are revolutionizing pallet structures. By mimicking patterns and structures found in nature, engineers are creating pallets that distribute loads more effectively and use materials more efficiently. This approach is leading to stronger, lighter, and more sustainable pallet designs.
Honeycomb structures inspired by beehives are being incorporated into pallet designs for improved strength-to-weight ratios. These structures allow for maximum strength with minimal material use, a crucial factor in reducing both costs and environmental impact. Leaf vein patterns are influencing the development of more efficient load-bearing structures in plastic pallets, mimicking nature’s own solutions for distributing weight and resources.
Perhaps most intriguingly, biomimetic adhesives based on gecko feet are being explored for creating stronger, more durable pallet joints. These adhesives could potentially revolutionize how pallets are constructed, offering superior strength without the need for traditional fasteners.

Source: researchgate.net
Smart Pallets and IoT Integration
The integration of sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) technology is transforming pallets from passive platforms to active participants in the supply chain. These smart pallets enable real-time tracking and condition monitoring, providing valuable data throughout their journey.
RFID tags and GPS sensors are being embedded in pallets to provide real-time location tracking. This technology allows companies to monitor their inventory with unprecedented accuracy, reducing losses and improving efficiency. Temperature and humidity sensors in smart pallets help monitor environmental conditions for sensitive cargo, ensuring that products arrive in optimal condition.
Blockchain technology is being used to create immutable records of pallet movements and transactions. This innovation enhances transparency and security throughout the supply chain, reducing fraud and improving accountability. The potential applications of blockchain in pallet management are vast, and we’re only beginning to scratch the surface of what’s possible.
[This video provides an overview of IoT-enabled smart pallets and their benefits in supply chain management.]
[Video Source: YouTube]
The Circular Economy of Pallets
The pallet industry is at the forefront of embracing circular economy principles. This approach considers the entire lifecycle of pallets, from production to end-of-life, with a focus on reuse, repair, and recycling. It’s not just about being environmentally friendly; it’s about creating a more efficient and sustainable business model.
Closed-loop pallet systems can reduce wood waste by up to 95% compared to single-use pallets. That’s a staggering figure that demonstrates the potential impact of circular economy principles in this industry. Advanced sorting technologies using machine vision and AI are improving the efficiency of pallet recycling processes, allowing for more accurate and rapid sorting of pallets for repair or recycling.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies are being conducted to quantify the environmental impact of different pallet materials and designs. These studies provide valuable insights that help companies make more informed decisions about their pallet choices. For instance, a recent study shows that an average plastic pallet can take about 100 trips before needing to be recycled, while the lifespan of the typical wood-block pallet is closer to 25 trips. [Source: https://www.inboundlogistics.com/articles/todays-pallets-leaders-of-the-stack/]
For those interested in implementing more sustainable business practices, our article on Navigating the E-commerce Frontier covers eco-friendly strategies for online retailers that can be applied to pallet management as well.
| Pallet Type | Average Lifespan (Trips) | Recyclability | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | 25 | High | Medium |
| Plastic | 100 | Medium | Low |
| Metal | 250+ | High | High |
Pallet Upcycling Initiatives
Innovative programs are finding new ways to repurpose end-of-life pallets. From furniture to art installations and building materials, these initiatives are creating value beyond the pallet’s primary use and reducing waste in the process. It’s a fascinating intersection of sustainability and creativity that’s catching on in various industries.
Thermal treatment processes are being developed to convert wood pallets into biochar for soil amendment. This process not only gives new life to old pallets but also contributes to soil health and carbon sequestration. CNC machines are being used to transform pallet wood into precision-cut components for furniture manufacturing, creating high-value products from what was once considered waste.
Chemical processes are being explored to break down plastic pallets into raw materials for new products. This closed-loop approach ensures that even at the end of their life cycle, plastic pallets continue to provide value rather than ending up in landfills.

Source: blogspot.com
Closed-Loop Pallet Systems
Closed-loop pallet systems are gaining traction in the industry, and for good reason. These systems involve continuously reusing pallets within a controlled network, offering both economic and environmental benefits. However, implementing such systems comes with its own set of challenges that require careful planning and execution.
RFID tracking systems are essential for managing closed-loop pallet pools, with read rates exceeding 99.9%. This level of accuracy ensures that pallets can be tracked and managed efficiently throughout their lifecycle. Automated cleaning and inspection systems using high-pressure water jets and machine vision can process up to 600 pallets per hour, categorizing them for repair or recycling with incredible speed and accuracy.
Predictive maintenance algorithms are being developed to optimize pallet repair schedules and reduce downtime. By anticipating when a pallet will need maintenance, companies can proactively address issues before they become problems, extending the life of their pallet fleet and reducing overall costs.
I recently spoke with a large retailer who implemented a closed-loop pallet system in their distribution network. The results were impressive: a 30% reduction in pallet-related costs and a 40% decrease in pallet loss over the course of a year. This system also improved inventory accuracy and reduced product damage during transit, demonstrating the wide-ranging benefits of closed-loop systems.
Biodegradable Pallet Materials
The search for more environmentally friendly pallet materials has led to the development of biodegradable options. These materials aim to provide the strength and durability required for logistics while reducing long-term environmental impact. It’s an exciting area of research that could potentially revolutionize the industry.
Biodegradable plastics derived from corn starch or sugarcane are being tested for pallet production. These materials offer the durability of traditional plastics but break down more readily at the end of their life cycle. Mycelium (fungal root structures) is being explored as a natural, biodegradable binding agent for wood fiber pallets. This innovative approach leverages nature’s own recycling systems to create truly sustainable pallets.
Accelerated weathering tests are used to simulate long-term environmental exposure and assess biodegradation rates. These tests help ensure that biodegradable pallets will perform as expected throughout their lifecycle and break down appropriately when disposed of.

Source: amesonpak.com
The Psychology of Pallet Management
Effective pallet management isn’t just about logistics and engineering; it also involves understanding human factors. From decision-making processes to the impact of design on worker safety and ergonomics, psychology plays a crucial role in optimizing pallet operations. It’s a fascinating aspect of the industry that often goes overlooked.
Cognitive load theory is being applied to pallet handling processes to reduce mental strain on warehouse staff. By designing systems and processes that minimize cognitive load, we can improve efficiency and reduce errors in pallet handling operations. Eye-tracking studies are being conducted to optimize pallet label designs and placement for quicker identification. These studies provide valuable insights into how workers interact with pallets and how we can design them to be more user-friendly.
Understanding the psychological aspects of pallet management can lead to significant improvements in operational efficiency. For those interested in optimizing their operations, our guide on Mastering the Art of Online Clothing Sales offers insights on streamlining inventory management and order fulfillment that can be applied to pallet management as well.
Cognitive Load in Pallet Handling
The design of pallets and management systems can significantly affect the mental workload of warehouse staff and forklift operators. By understanding and optimizing these cognitive factors, we can improve efficiency and reduce errors in pallet handling operations. It’s a delicate balance between providing necessary information and avoiding information overload.
EEG (electroencephalogram) studies are being used to measure cognitive load during pallet handling tasks. These studies provide real-time data on brain activity, allowing researchers to identify which tasks are most mentally demanding and where improvements can be made. Virtual reality simulations are being developed to train operators in complex pallet stacking scenarios without physical risk. These simulations allow for safe, repeated practice of challenging tasks, improving skill and confidence.
Machine learning algorithms are being employed to analyze operator behavior and suggest workflow optimizations. By identifying patterns and inefficiencies in how workers interact with pallets, these algorithms can provide valuable insights for improving processes and reducing cognitive load.
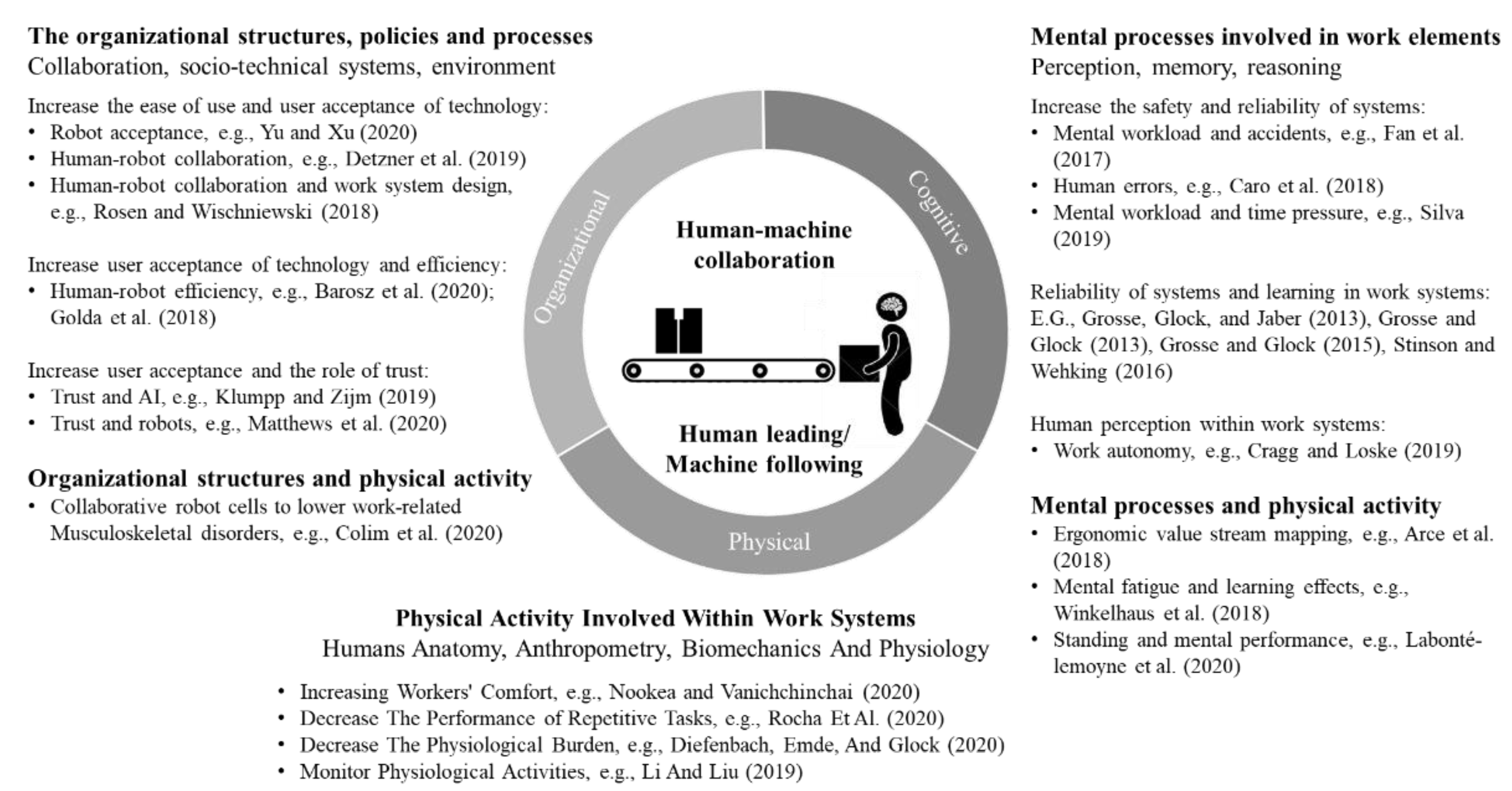
Source: mdpi.com
Color Psychology in Pallet Identification
Color coding plays a significant role in pallet management. The strategic use of colors can improve efficiency and reduce errors in logistics operations by making identification and sorting processes more intuitive. It’s a simple yet effective way to streamline operations and reduce cognitive load on workers.
Spectrophotometers are used to ensure Spectrophotometers are used to ensure consistent color matching across pallet production batches. This precision is crucial for maintaining an effective color-coding system. Studies have shown that color-coded pallets can reduce picking errors by up to 30% in warehouse operations, a significant improvement in accuracy and efficiency.
UV-resistant pigments are being developed to maintain color integrity under prolonged sun exposure. This innovation ensures that color-coded pallets remain easily identifiable even when used in outdoor environments or exposed to harsh lighting conditions.
Ergonomic Considerations in Pallet Design
The physical design of pallets directly impacts worker posture, movement, and overall well-being. Ergonomic pallet designs can reduce the risk of injury and improve productivity in material handling environments.
Motion capture technology is being used to analyze worker movements during pallet handling tasks. This data provides valuable insights into the physical demands of pallet handling and helps identify areas for ergonomic improvement. Anthropometric data from diverse populations is informing the development of more inclusive pallet designs, ensuring that pallets are suitable for workers of various sizes and physical capabilities.
Finite element analysis is being applied to optimize pallet structures for improved ergonomics without compromising strength. This advanced modeling technique allows engineers to create pallets that are both sturdy and easy to handle, reducing the physical strain on workers.
Decision Support Systems in Pallet Management
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing pallet management decision-making processes. These technologies are being used to optimize pallet selection, routing, and inventory management, leading to more efficient and cost-effective operations.
Neural networks are being trained on historical data to predict optimal pallet types for specific shipping routes. This predictive capability allows companies to make informed decisions about pallet selection, reducing costs and improving efficiency. Genetic algorithms are being used to solve complex pallet loading optimization problems, ensuring that cargo is packed efficiently and securely.
Natural language processing is being applied to analyze shipping documents and automate pallet requirement forecasting. This technology can quickly process vast amounts of unstructured data, providing accurate predictions of pallet needs based on upcoming shipments.
Predictive Analytics for Pallet Demand
Advanced analytics are transforming how businesses forecast their pallet needs. By leveraging historical data and market trends, companies can more accurately predict demand, reducing overstock and stockouts in dynamic supply chains.
Time series analysis techniques like ARIMA (AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average) are being used to forecast pallet demand. These sophisticated statistical methods can identify patterns and trends in historical data, providing accurate predictions of future pallet needs.
Machine learning models incorporating external factors such as weather patterns and economic indicators are improving forecast accuracy. By considering a wide range of variables, these models can provide more nuanced and reliable predictions than traditional forecasting methods.
Real-time data streaming and edge computing are enabling dynamic adjustments to pallet inventory levels. This technology allows companies to respond quickly to changes in demand, optimizing their pallet inventory in real-time.
Source: nexocode.com
Geopolitical Implications of Pallet Standards
Pallet standards and regulations have far-reaching effects on international trade and cross-border logistics. Understanding the global landscape of pallet requirements is crucial for businesses operating in multiple markets.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed over 20 standards related to pallet dimensions and testing methods. These standards aim to create a common framework for pallet design and usage across different countries and industries.
According to industry data, China was the world’s largest pallet producer in 2023, followed by the US. These two countries have the world’s largest domestic markets for pallets by far. [Source: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2024/10/28/2969826/28124/en/Pallets-Market-Report-2024-2033-Efforts-to-Address-Sustainability-Concerns-Reshaping-Markets-Further-Opportunities-for-Smart-Pallets.html]
Pallet Diplomacy
The negotiation of pallet standards between countries and trade blocs is a complex process with significant implications for global commerce. These negotiations often involve balancing economic interests, safety concerns, and logistical efficiency.
Bilateral trade agreements often include specific clauses regarding acceptable pallet standards and materials. These clauses can have significant impacts on trade flows and logistics operations between countries. The World Trade Organization (WTO) has been involved in settling disputes related to pallet regulations as potential trade barriers, highlighting the importance of pallet standards in international trade.
Harmonization efforts are underway to develop a global pallet standard, with challenges including varying truck bed dimensions and warehouse racking systems. While a truly global standard remains elusive, these efforts are crucial for facilitating smoother international trade and logistics operations.
| Region | Standard Pallet Size (mm) | Common Material | Key Regulations |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | 1219 x 1016 | Wood | ISPM-15 for international shipments |
| Europe | 1200 x 800 (EUR-pallet) | Wood | EPAL certification, chemical treatment |
| Asia | 1100 x 1100 | Plastic | Varies by country, focus on hygiene |
| Australia | 1165 x 1165 | Wood | AS 4068-1993 standard |
Pallet Tariffs and Trade Wars
Pallets have occasionally become caught in the crossfire of international trade disputes. Understanding the historical and current instances where pallets have been subject to tariffs or trade restrictions is crucial for navigating the global logistics landscape.
In 2018, the U.S. imposed a 10% tariff on Chinese wooden pallets as part of broader trade tensions. This move had significant ripple effects throughout the supply chain, affecting both pallet manufacturers and users. The EU has specific regulations on the treatment of wooden pallets to prevent the spread of plant pests, affecting import procedures. These regulations can create additional compliance costs for companies shipping to or from the EU.
Some countries have implemented preferential tariffs for pallets made from sustainable or recycled materials to promote environmental initiatives. These policies can influence material choices and manufacturing processes in the pallet industry.
Regional Pallet Preferences and Cultural Factors
Pallet design, materials, and management practices vary significantly across different parts of the world. These differences are often influenced by cultural norms, economic conditions, and local industry practices.
In Japan, plastic pallets are preferred due to strict hygiene standards in the food and pharmaceutical industries. This preference reflects Japan’s focus on cleanliness and precision in manufacturing and logistics. European pallets (EUR-pallets) are typically smaller than North American pallets due to differences in truck dimensions. This size difference can create challenges for companies operating in both markets.
In developing countries, manual pallet production methods are still common, influencing local pallet designs and materials. These methods often result in more varied pallet sizes and qualities, which can present challenges for standardization efforts.
The Rise of Plastic Pallets in Asia
The Asian market has seen a significant shift towards plastic pallets in recent years. This trend is driven by various factors, including hygiene requirements, durability needs, and changing environmental regulations.
The Asian plastic pallet market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.5% from 2021 to 2026. This rapid growth reflects the increasing adoption of plastic pallets across various industries in the region. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is the most commonly used material for plastic pallets in Asia due to its strength and chemical resistance. HDPE pallets offer a good balance of durability and cost-effectiveness, making them popular in many industries.
Automated injection molding processes are being used to produce plastic pallets with consistent quality and reduced labor costs. These advanced manufacturing techniques are helping to make plastic pallets more competitive with traditional wooden pallets in terms of cost and quality.
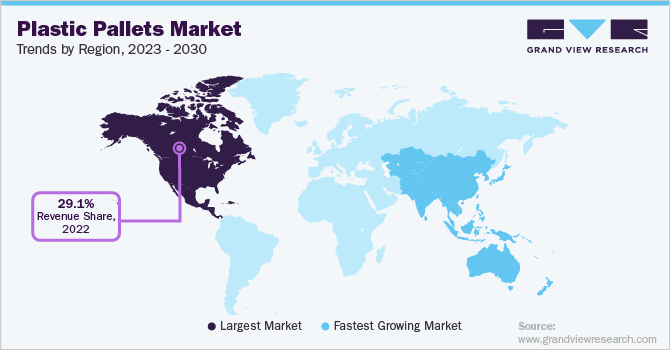
Source: grandviewresearch.com
Pallet Management Services: Beyond the Basics
The landscape of pallet management services is evolving rapidly. Companies are now offering innovative solutions that go far beyond traditional pallet pooling and repair, providing comprehensive supply chain optimization services.
The global pallet pooling market size was valued at $7.2 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $10.4 billion by 2028. This growth reflects the increasing recognition of the value of professional pallet management services in optimizing supply chain operations.
“The Pallet Book – Transforming Pallet Management” from StreetInsider reports on a new platform launched in May 2024 aiming to facilitate and simplify pallet transactions, addressing inefficiencies in the industry.
Value-Added Pallet Services
Pallet management companies are diversifying their offerings with a range of supplementary services. These additions aim to provide comprehensive solutions to their clients’ supply chain needs.
Advanced data analytics platforms offer real-time insights into pallet usage and supply chain efficiency. These platforms can help companies identify bottlenecks, optimize pallet flows, and reduce costs. Carbon offset programs are being integrated with pallet services to support sustainability goals. These programs allow companies to offset the environmental impact of their pallet usage, contributing to their overall sustainability efforts.
Customized pallet design services utilize 3D printing for rapid prototyping and testing. This technology allows for quick iteration and optimization of pallet designs, reducing development time and costs.
A leading electronics manufacturer partnered with a pallet management service to implement a customized tracking system. This collaboration resulted in a 25% reduction in lost pallets and a 15% improvement in inventory accuracy across their distribution network. The success of this project demonstrates the potential value of advanced pallet management services in improving overall supply chain efficiency.
Pallet-as-a-Service (PaaS) Models
Subscription-based pallet management services are gaining momentum. These PaaS models present flexible, scalable solutions adaptable to the evolving needs of businesses across various scales.
PaaS models often leverage IoT-enabled pallets to provide real-time tracking and usage data. This technology allows for more accurate billing based on actual usage and helps companies optimize their pallet inventory. Machine learning algorithms optimize pallet allocation and predict maintenance needs. By anticipating when and where pallets will be needed, these algorithms can help reduce transportation costs and improve overall efficiency.
Blockchain technology ensures transparent and secure transactions within PaaS platforms. This technology can help reduce disputes and improve trust between pallet providers and users.
Integrated Supply Chain Consulting
Pallet management companies are expanding their roles to offer comprehensive supply chain optimization services. By leveraging their expertise in pallet logistics, these firms are assisting clients in enhancing overall supply chain efficiency.
Digital twin technology creates virtual models of clients’ supply chains for scenario planning and optimization. These models allow companies to test different strategies and configurations without disrupting their actual operations. Advanced simulation software analyzes and optimizes pallet flow throughout the entire supply chain. By identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies, this software can help companies make data-driven decisions to improve their operations.
Artificial intelligence identifies patterns and inefficiencies in supply chain data, providing actionable insights. These insights can help companies make more informed decisions about their pallet management strategies and overall supply chain operations.
Source: smartsheet.com
Technology Integration in Pallet Services
Cutting-edge technologies are being adopted by pallet management companies to enhance their service offerings and operational efficiency. These advancements are transforming how pallets are tracked, maintained, and optimized throughout their lifecycle.
5G networks enable real-time communication between smart pallets and management systems. This high-speed, low-latency connectivity allows for more accurate tracking and faster response times to changes in pallet demand or location. Cloud computing platforms process and analyze vast amounts of pallet-related data. These platforms provide the computational power needed to run complex analytics and machine learning algorithms on pallet usage data.
Robotic process automation (RPA) streamlines administrative tasks in pallet management. By automating routine tasks such as data entry and report generation, RPA frees up human workers to focus on more strategic activities.
Blockchain for Pallet Traceability
Blockchain technology is creating transparent, immutable records of pallet movements and transactions throughout the supply chain. This innovation enhances traceability, reduces fraud, and improves overall supply chain visibility.
Distributed ledger technology ensures tamper-proof pallet transaction records accessible to authorized parties. This transparency can help reduce disputes and improve trust between different parties in the supply chain. Smart contracts automate pallet rental agreements and payment processes. These self-executing contracts can streamline transactions and reduce administrative overhead.
Blockchain-based systems provide end-to-end visibility of a pallet’s journey, from manufacturer to end-user. This comprehensive tracking can help companies identify inefficiencies and optimize their pallet usage.
AI-Powered Pallet Inspection Systems
Artificial intelligence and computer vision are revolutionizing pallet quality control and repair processes. These technologies enable faster, more accurate inspections and help optimize maintenance schedules.
Deep learning algorithms detect subtle defects in pallets that might be missed by human inspectors. These algorithms can analyze images of pallets in real-time, identifying issues such as cracks, splinters, or missing components. High-speed cameras and AI processing can inspect up to 1,000 pallets per hour with 99% accuracy. This speed and accuracy far surpass what is possible with manual inspections.
Predictive maintenance models use historical data and AI to forecast when pallets will need repair or replacement. By anticipating maintenance needs, companies can proactively address issues before they lead to pallet failures or damage to goods.
The Environmental Impact of Pallet Choices
The selection of pallet materials and designs has significant environmental implications. Understanding the ecological footprint of different pallet options is crucial for making sustainable decisions in supply chain management.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) studies show that wooden pallets generally have a lower carbon footprint compared to plastic pallets over their lifetime. However, this advantage can vary depending on factors such as transportation distances, reuse rates, and end-of-life disposal methods.
Life Cycle Assessment of Pallet Materials
Comparing the environmental impacts of wood, plastic, and metal pallets requires a comprehensive life cycle assessment. This analysis considers factors such as carbon footprint, water usage, and recyclability from production to end-of-life.
ISO 14040 and 14044 standards are used to conduct standardized life cycle assessments of pallet materials. These standards ensure that LCA studies are conducted in a consistent and scientifically rigorous manner. Energy consumption for producing a standard wooden pallet is approximately 25% lower than that of a plastic pallet. However, plastic pallets often have longer lifespans, which can offset this initial energy difference over time.
Metal pallets have the highest initial environmental impact but can last up to 10 times longer than wooden pallets. This longevity can make metal pallets a more environmentally friendly choice in certain high-use scenarios.
Pallet Recycling Technologies
Innovative methods for recycling different pallet materials are constantly being developed. These technologies aim to maximize material recovery and minimize waste in the pallet lifecycle.
Advanced optical sorting systems can separate different types of plastic pallets with 99% accuracy. This high level of sorting accuracy ensures that recycled materials maintain their quality and value. Pyrolysis technology is being used to convert non-recyclable plastic pallets into fuel oil and carbon black. This process provides a way to recover value from pallets that would otherwise end up in landfills.
Wood fiber recovery techniques can reclaim up to 95% of usable material from damaged wooden pallets. This high recovery rate helps to minimize waste and reduce the demand for new wood in pallet production.
Carbon Sequestration in Wooden Pallets
Wooden pallets possess a unique characteristic: they store carbon throughout their lifecycle. This attribute becomes particularly significant when the wood is sourced from sustainably managed forests, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
A standard wooden pallet can sequester approximately 28 kg of CO2 over its lifetime. This carbon storage helps to offset some of the emissions associated with pallet production and transportation. Sustainable forest Sustainable forest management practices ensure that for every tree harvested for pallet production, multiple new trees are planted. This approach helps maintain forest cover and continues the cycle of carbon sequestration.
Advanced carbon accounting methods are being developed to accurately quantify the carbon storage potential of wooden pallets in supply chains. These methods will help companies better understand and report on the environmental impact of their pallet choices.
Pallet Pooling and Environmental Benefits
Pallet pooling systems are making significant strides in reducing waste and improving resource efficiency within the logistics industry. These systems promote the continuous reuse of pallets, minimizing the need for new production and disposal.
Pallet pooling can reduce wood waste by up to 70% compared to single-use pallet systems. This reduction in waste translates to fewer trees being harvested and less material ending up in landfills. Advanced tracking technologies in pooling systems can increase pallet utilization rates by up to 20%. Higher utilization rates mean fewer pallets are needed overall, further reducing environmental impact.
Life cycle studies show that pooled pallets can have a 50% lower environmental impact compared to non-pooled alternatives. This significant reduction is due to the extended lifespan and more efficient use of pallets in pooling systems.
Reverse Logistics in Pallet Management
Efficient reverse logistics systems for pallet recovery and reuse are proving to be both environmentally and economically beneficial. These systems ensure that pallets are collected, refurbished, and reintroduced into the supply chain effectively.
Automated sorting facilities can process up to 1,000 pallets per hour, categorizing them for repair or recycling. This high-speed sorting capability allows for more efficient recovery and reuse of pallets. GPS-enabled tracking systems improve pallet recovery rates by up to 30% in complex supply chains. By knowing the exact location of pallets, companies can more effectively plan their recovery and reuse.
Reverse logistics optimization algorithms can reduce empty truck miles by up to 25%, lowering transportation-related emissions. These algorithms help companies plan more efficient routes for pallet recovery, reducing the environmental impact of transportation.
Green Pallet Initiatives
The pallet industry is spearheading various programs and certifications aimed at promoting environmentally friendly practices and materials. These initiatives are driving innovation and sustainability across the sector.
The Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI) certification ensures that wooden pallets come from responsibly managed forests. This certification helps companies verify that their pallet choices are supporting sustainable forestry practices. Cradle-to-Cradle certification is being pursued by some pallet manufacturers, ensuring products are fully recyclable or biodegradable. This certification takes a holistic approach to product sustainability, considering factors beyond just end-of-life disposal.
Carbon neutral pallet programs are emerging, offsetting emissions through reforestation and renewable energy projects. These programs allow companies to mitigate the environmental impact of their pallet usage while supporting broader sustainability initiatives.
The Role of Pallets in Disaster Relief and Humanitarian Logistics
Pallets play a crucial, often overlooked role in emergency response scenarios. Specialized pallet management strategies can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of humanitarian aid efforts.
Humanitarian logistics operations handle an estimated 60-80% of costs in disaster relief efforts. Efficient pallet management can help reduce these costs and improve the speed and effectiveness of aid delivery.
Rapid Deployment Pallet Systems
Innovative pallet designs are facilitating quick assembly and deployment in disaster-stricken areas. These systems are crucial for the swift distribution of essential supplies in challenging environments.
Foldable pallets can reduce storage space by up to 75%, allowing for more efficient pre-positioning of resources. This space-saving feature is particularly valuable in disaster preparedness, where storage space is often limited. Lightweight composite materials are being used to create pallets that are 30% lighter than traditional wooden ones, easing air transport. These lighter pallets are especially useful in situations where air drops are necessary for aid delivery.
Modular pallet designs allow for on-site assembly, reducing transportation costs for disaster relief organizations. These designs provide flexibility in how pallets are transported and assembled, adapting to the specific needs of each disaster response scenario.
Collapsible Pallets for Air Transport
The use of lightweight, collapsible pallets in air freight operations is revolutionizing emergency supply delivery. These specialized pallets maximize cargo space while minimizing weight, crucial factors in urgent humanitarian missions.
Collapsible air pallets can increase usable cargo space by up to 40% compared to rigid alternatives. This increased capacity allows for more aid supplies to be transported in a single flight. Advanced polymer composites are being used to create pallets that weigh 50% less than traditional aluminum air pallets. The weight reduction translates to fuel savings and increased payload capacity for aid flights.
Self-locking mechanisms in collapsible pallets can reduce assembly time by up to 75%, speeding up loading processes. This rapid assembly capability is crucial in time-sensitive disaster response situations.
Water-Resistant Pallets for Flood Zones
Specialized pallet materials and coatings are being developed to withstand prolonged exposure to water in flood-prone regions. These innovations ensure that critical supplies remain protected and accessible during water-based disasters.
Hydrophobic coatings can maintain pallet integrity for up to 72 hours of continuous water exposure. This durability is essential for keeping aid supplies dry and usable in flood conditions. Closed-cell foam materials are being used to create buoyant pallets that can float with up to 1,000 kg of cargo. These floating pallets can be crucial for transporting supplies in flooded areas where traditional transportation methods are impossible.
Antimicrobial treatments are being applied to water-resistant pallets to prevent mold growth in humid conditions. This feature helps maintain the quality and safety of aid supplies in challenging environmental conditions.
Pallet-Based Temporary Structures
In humanitarian crisis situations, pallets are being repurposed to create temporary shelters, medical facilities, and distribution centers. This innovative approach provides rapid, cost-effective solutions for immediate infrastructure needs.
A standard pallet shelter can be assembled by two people in under 30 minutes, providing immediate housing for disaster victims. The speed and simplicity of assembly make these structures invaluable in the immediate aftermath of a disaster. Interlocking pallet designs allow for the construction of structures up to two stories high without additional fasteners. This versatility enables the creation of more complex and functional temporary buildings.
Thermal insulation techniques are being developed to improve the comfort and energy efficiency of pallet-based structures. These advancements help create more livable conditions in temporary shelters, particularly in extreme climates.
Modular Pallet Building Systems
Standardized pallet designs that can be easily assembled into functional structures are gaining traction in emergency response scenarios. These systems provide versatile solutions for temporary housing and storage needs.
Modular pallet systems can create structures ranging from 10 to 100 square meters using a single standardized component. This flexibility allows for the rapid construction of various types of buildings to meet different needs in disaster zones. Computer modeling is used to optimize pallet-based structures for different climate conditions and load requirements. This approach ensures that temporary structures are safe and suitable for their intended use and location.
Rapid prototyping techniques allow for on-site customization of pallet structures to meet specific local needs. This adaptability is crucial in disaster response, where conditions and requirements can vary widely between different locations and situations.
Pallet-Based Water Filtration Systems
Innovative uses of pallets in creating portable water filtration and distribution systems are emerging as crucial tools in disaster relief efforts. These systems leverage the inherent strength and modularity of pallets to provide clean water in challenging environments.
A single pallet-based filtration unit can provide clean water for up to 500 people per day. This high capacity makes these systems invaluable in areas where traditional water infrastructure has been compromised. Solar-powered pumps integrated into pallet structures can operate autonomously in areas without electricity. This feature ensures continuous water supply even in regions with limited or no power infrastructure.
Nanotechnology-based filtration membranes are being incorporated into pallet systems, removing up to 99.9999% of waterborne pathogens. These advanced filtration technologies help ensure that the water provided is safe for consumption, preventing waterborne diseases in disaster-affected populations.
Learnings Recap
- Pallet management is a complex ecosystem that impacts global commerce and sustainability efforts
- Technological innovations, from IoT integration to AI-powered inspections, are revolutionizing the industry
- Environmental considerations are driving the development of new materials and circular economy practices
- Pallets play a crucial role in disaster relief, with specialized designs enhancing humanitarian logistics
- The psychological aspects of pallet management, including cognitive load and ergonomics, are increasingly recognized
- Geopolitical factors and regional preferences significantly influence pallet standards and practices globally
As we’ve explored the intricate world of pallet management, it’s clear that this field is far more complex and impactful than many realize. From technological innovations to environmental considerations and humanitarian applications, pallets are at the forefront of logistics evolution.
For those looking to optimize their pallet management strategies, Bulk By Pallet offers curated solutions that align with many of the advanced concepts we’ve discussed. Their focus on quality and sustainability can help address the challenges of efficient inventory management and waste reduction. Whether you’re a small business owner or a large-scale distributor, exploring their offerings could be a step towards more effective pallet management.
Ready to elevate your pallet management game? Visit Bulk By Pallet’s website to discover how their expertly curated pallets can streamline your operations and contribute to a more sustainable supply chain.





Add comment